
In today’s demanding industrial, medical, and scientific environments, labeling solutions must withstand a wide range of extreme conditions without compromising readability or adhesion. Labeling materials used in extreme environments like freezers, liquid nitrogen, and autoclaves face several challenges due to the harsh conditions. Here’s a breakdown by environment:
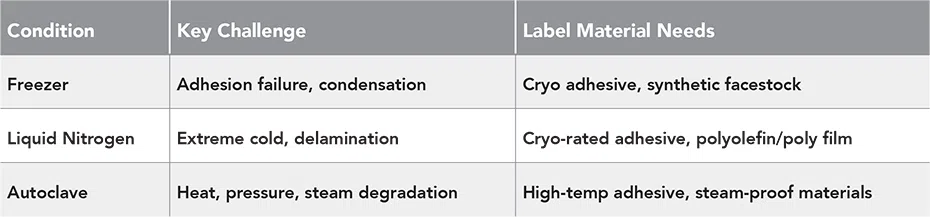
1. Freezer (-20°C to -80°C)
Challenges:
- Adhesive failure: Many labels lose adhesion at ultra-low temperatures.
- Cracking or brittleness: Some label materials (especially paper-based) can become brittle and crack.
- Condensation: Moving samples in and out of the freezer can cause moisture buildup, weakening adhesive and smudging print.
- Frost: Surfaces with frost or ice prevent proper label adhesion.
2. Liquid Nitrogen (-196°C)
Challenges:
- Extreme cold: Labels and adhesives must withstand deep cryogenic temperatures without delaminating or becoming unreadable.
- Adhesion at ambient before immersion: Labels need to stick before exposure—many fail during the freeze.
- Cracking or shattering: Incorrect label materials can shatter or peel in LN2.
- Resistance to phase changes: Immersion and thawing cycles can degrade standard labels.
3. Autoclave (121°C, high pressure, steam)
Challenges:
- High heat and pressure: Many adhesives melt or degrade.
- Steam and moisture: Causes labels to peel or print to run.
- Delamination: Label layers may separate.
- Ink fading or bleeding: Non-autoclave-safe printing methods fail.
Table of Conditions & Material Needs
Summary
In addition to the challenges associated with creating adhesives and label constructions that withstand such extreme environments, there were also issues related to ink adhesion to the label facestock.
In the past, water-based inkjet printing was not considered suitable for most extreme environments, especially freezers, liquid nitrogen, and autoclaves.
Common challenges encountered were the following:
- Freezers: Inks could smear or run due to condensation or humidity.
- Liquid Nitrogen: Ink often becomes brittle or fades, and the label adhesives may fail.
- Autoclave: Steam and heat can dissolve or blur the ink; the label may peel.
AstroNova partners with various industries to address labeling issues. Our pharmaceutical and healthcare clients needed water-based inkjet labels for laboratory environments that could withstand extreme temperatures.
AstroNova worked with a label material manufacturer and developed an industrial grade matte synthetic label material (Material # 236) with an inkjet-receptive face stock that features a cryogenic adhesive the requirements of a variety of applications.
At AstroNova’s request, an independent laboratory conducted testing on label material #236 to validate its performance under freezer, liquid nitrogen and autoclave conditions.
At AstroNova’s request, an independent laboratory conducted testing on label material #236 to validate its performance under freezer, liquid nitrogen and autoclave conditions. Samples were printed with QuickLabel printers using water-based pigment inks (used in models Kiaro!D / QL-120D / QL-120De). Printed samples were tested by the independent lab in Freezer, Liquid Nitrogen, and Autoclave conditions on several different substrates.

Test Methods
- Freezer: @ -80°C (-112°F): Three cycles of 16 hours at -80°C then 8 hours at 22°C
- Liquid Nitrogen: @ -196°C (-321°F): Three cycles of 4 hours at -196°C then 20 hours at 22°C
- Autoclave: @ 121°C (250°F): Three cycles of 20 minutes at 121°C @ 35PSI then 1 hour at 22°C
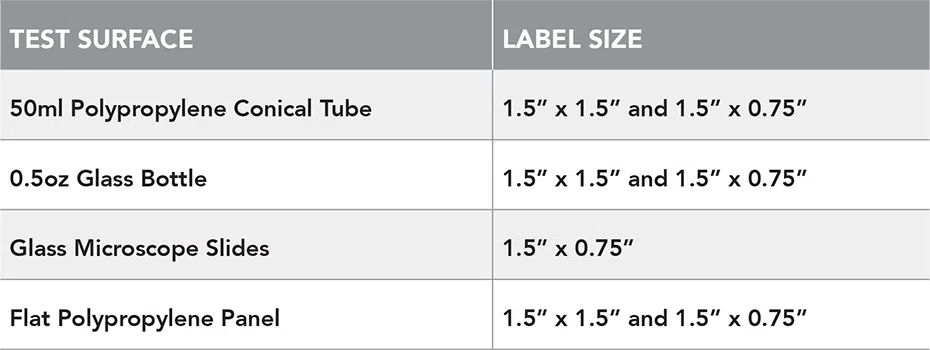
Test Surfaces and Label Sizes
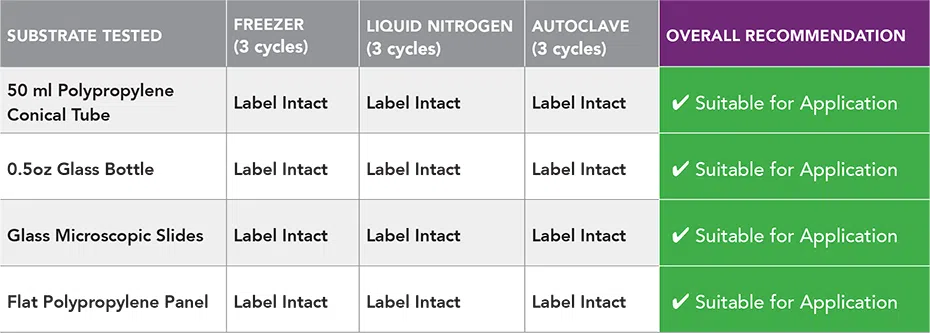
Test Results & Recommendations
Observations
- All labels remained adhered to all the tested surfaces throughout the three cycles of exposure.
- No bleeding was observed as a result of exposure to frozen and autoclave environments
- No color fading was detected after exposure to freezing or autoclave environments.
- This test data is provided solely to demonstrate the label It is the customer’s sole and exclusive responsibility to confirm the product’s suitability for their specific application.
Photos: Control and After Three Test Cycles
- Photos show comparison of Control samples to Tested samples after three (3) cycles in Liquid Nitrogen, -80 °C Freezer, and Autoclave environments to show no effects on print quality.
- There were no issues with label adhesion on any of the surfaces in any of the environments.






